MONETARY POLICY
Greenland enters, like the Faroe Islands, into a monetary union with Denmark. The National Bank of Denmark is responsible for the monetary policy in the union.
Denmark pursues a fixed exchange rate policy with regard to the Euro. This means that the monetary and currency policy aims to stabilise the exchange rate between Danish kroner and Euros.
The developments in the actual exchange rate against the Euro appear in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Exchange Rates of Danish Kroner Against the Euro
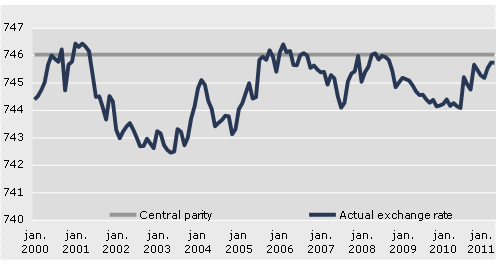
Source: The National Bank of Denmark
The exchange rates of other currencies in the world, primarily US dollars, yen, and pounds, are determined by market forces. Developments in these currencies play a major role for the prices at which the exports of Greenland such as fish and shellfish can be sold abroad (the competitive power) and the prices at which oil can be imported.
Figure 2
Index for the Exchange Rate of Kroner Against Dollars, Pounds, and Yen
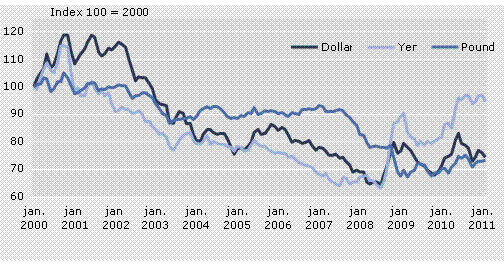
Source: The National Bank of Denmark
Link
Read more about the National Bank of Denmark and its monetary policy at www.nationalbanken.dk.